2025

Documentation
Camera Calibration
1. Create a python script named camera_calibration.py
import cv2
from ultralytics import YOLO
import math
model = YOLO("C:\\Users\\<USER>\\Desktop\\OpenML\\high.pt") #Modify here with your current Path and the downloaded OpenML model
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0) #If it doesn't work, increment the number by 1 until the camera works and appears on the screen
while True:
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
results = model.predict(frame, conf=0.5)
frame_with_results = results[0].plot()
boxes = results[0].boxes
if len(boxes) > 0:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = map(int, boxes.xyxy[0])
object_width = x2 - x1
object_height = y2 - y1
cv2.putText(frame_with_results, f"Obj Width: {object_width:.2f}",
(x1, y1 + 40),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(frame_with_results, f"Obj Height: {object_height:.2f}",
(x1, y1 + 60),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow('OpenML - Real-time Detection', frame_with_results)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'): # Press Q to exit the code
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()2. To calculate the orientation of the sample, minWidth, maxWidth,
minHeight, maxHeight must be measured
1. Place the sample straight in the image
2. Make sure the sample is completely
in the image. It is essential that the sample fits in the image and is not half out of the image
Example:

3. Now rotate the sample to a 90-degree angle, and then note
maxWidth, maxWidth. Make sure the sample is completely in the image
Example:
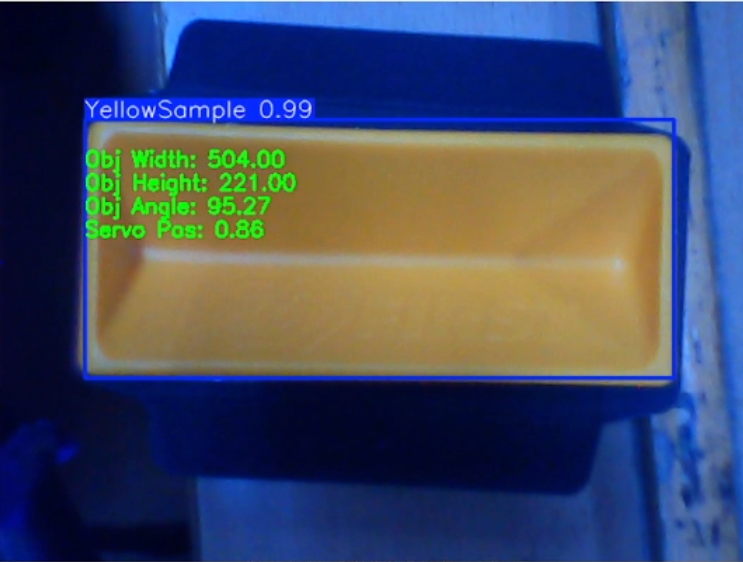
2.Mathematical application of measurements
1. After minWidth, minHeight, maxWidth, maxHeight have been
measured, we must apply them mathematically to find the sample orientation
Let's imagine there is a diagonal in this rectangle created by ML. We calculate the angle
between the diagonal and the width.
From here we can apply the arctan function from mathematics to calculate the angle.
We divide width by height => arctan(width/height) resulting in an angle.
Now we do the calculations for when the sample was straight (minWidth, minHeight).
The angle given by arctan when the sample is straight
is 24.79 degrees
We do the same for when the sample is at 90 degrees. (maxWidth, maxHeight)
The angle given by arctan when the sample is at a 90-degree
angle is 66.32 degrees
Let's take the example that the Intake at position 0.5 is perfectly straight and can only take
samples in a straight position
The Intake position must be measured when it is 90 degrees to the left and similarly when it is
90 degrees to the right
Position 0.15 is the 90-degree angle to the left of the Intake.
Position 0.85 is the 90-degree angle to the right of the Intake.
Thus we know that 0.85-0.5 = 0.35 has a rotation of 90 degrees. So we divide 0.35 by 90 degrees
0.35/90 degrees = 0.0038 Intake position/degree. So for every 0.0038 added to the Intake
position, the Intake moves 1 degree to the right
This formula can also be applied to other Intakes with different servo positions.
math.degrees(math.atan(object_width / object_height))2. After finding the angle when the sample is straight and at 90
degrees, we must use a mathematical formula to find the true angle of the sample
We subtract the initial angle when the sample was straight (the smallest angle) from the
angle given by arctan.
orientation_angle = (arctg(object_width/object_height) - 24.79) / y
And y is the maximum angle (sample is at 90 degrees) - minimum angle (sample is straight) /
90 degrees
y = (66.32 - 27.79)/90 => y = 0.45955
We apply the final formula and it results in (In Python):
Final mathematical formula: [arctg(object_width/object_height)-24.79]/0.45955
orientation_angle = (math.degrees(math.atan(object_width/object_height))-24.79)/0.459553. Calculating the Intake position based on the sample angle (Servo Intake)
After you have finished calibrating the camera, go back to Getting
Started
Setup
2D Sample Detection
Camera Calibration
3D Sample Detection
Training ML
Examples